Dust Mites
You cannot see dust mites in your home, but they can definitely have an impact on your life, making it important to learn how to deal with them.
Biology of Dust Mites
House dust mites are only around 0.5 mm long as fully mature adults and they are even smaller when still immature. Because of this small size, you cannot see dust mites without a microscope. If you happen to have one handy, you will notice that dust mites have a globular shape with creamy white or clear coloring and hairs on the body and legs. In the United States, you are likely to come across one of two species of dust mites, the North American or the European house dust mite.
In order to develop, dust mites need very specific environmental conditions to be met. They grow and develop best between temperatures of 75 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit and relative humidity levels of 70 to 80 percent. Dust mites will lose and absorb moisture via their skin. They are also at high risk of dehydration. Because of this, they typically have a low chance of survival in homes where the relative humidity is under 50 percent. Most homes in the country, however, can support house dust mites without a problem.
The main source of food for dust mites is the skin scales or dander in normal house dust. The mites will typically be most numerous in areas with the most people and pet activity, such as beds, chairs, and nearby carpets. Conveniently for the mites, these areas also have higher relative humidity from perspiration and exhalation.
Throughout their lives, dust mites pass through five stages. They begin as an egg, before becoming a larva, then a protonymph, a tritonymph, and finally an adult. Each stage is separated by a molt. In optimum conditions, the development cycle will take around a month and adults live one or two months. Females lay around 50 eggs during this time.
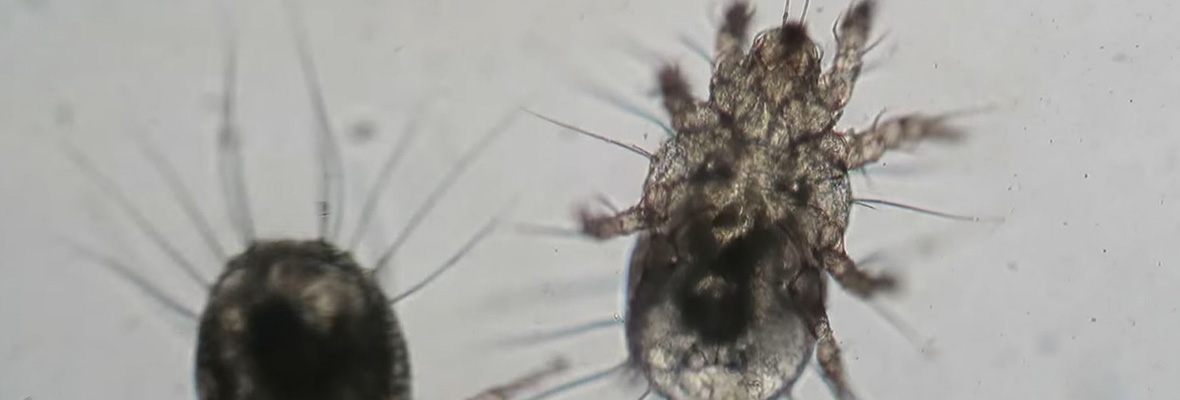
Why Dust Mites Are Considered Pests
The biggest issue related to dust mites is irritation and allergies. Many people have reactions to allergenic proteins that cause symptoms, with those proteins actually in the mites. When the tiny particles are airborne from regular household activity, they are inhaled, leading to an allergic reaction.
In addition to affecting those with allergies, dust mites can also worsen the symptoms of those who suffer from asthma. In fact, dust mites are among the biggest indoor triggers for people with asthma or allergies. Even those without either condition may be sensitive to dust mites. Those who experience ongoing exposure to the dust mites can have mild to severe reactions.
Mild reactions to dust mites can include sneezing, watery eyes, and a runny nose on occasion. Severe reactions can have persistent systems such as coughs, facial pressure, congestion, and sneezing as well as severe asthma attacks.
Methods for Controlling Dust Mites
The best method for controlling dust mites is to reduce the number of areas and the overall surface area of places they can grow. This means replacing the furniture that is soft with items that have smooth surfaces. Swap out your drapes or curtains for blinds. Additionally, you should cover your pillows and mattresses.
If you have a severe reaction to dust mites, then it will be a very smart move to get rid of the carpets in your house. This can be a time-consuming and expensive process, so start with the areas that the person with the sensitivities spends the most time in.
Interestingly enough, cockroaches have also been linked to dust mites and dust mite allergies. That is because microscopic particles from cockroaches are commonly found in household dust. As such, a pest control professional who can kill and prevent cockroaches on your property will also be able to assist with dust mite control.
Certain pest control methods also work on dust mites, with some studies indicating that diatomaceous earth is a good natural pesticide for dust mites. You can also ask your pest control professional if they know of any other pesticides that target these mites.
DIY Tips for How to Get Rid of Dust Mites
The first thing you should do if you are sensitive to dust mites in your home is to reduce the level of humidity. If possible, try to keep the humidity level below 50 percent as this will make it very challenging for dust mites to survive. If you live in a humid area, this means that you should use a dehumidifier and air conditioning. When the weather is dry, you can further remove humidity by opening the windows for about an hour daily.
To keep dust mites from accumulating on bedding and furniture, make sure to thoroughly clean everything at least once a week. For bedding and similar items, this means washing them using hot water. Follow this up with high dryer temperatures of at least 200 degrees Fahrenheit. For furniture and floors, this means vacuuming. If you have to keep the carpet, then get a vacuum that has a high-efficiency filter. You should make sure to use a damp cloth or damp mop for dusting as dry dusting will stir up dust mites into the air.
Another simple switch to help reduce dust mites is to swap out your current bedding with hypoallergenic bedding. This bedding has a design that is tightly woven with smaller pore sizes. This makes it almost impossible for mites to get into the material, dramatically reducing the number of dust mites in your bedroom.
You can also try swapping out your polyester fiber pillows with those made with natural feathers. Some studies have indicated dust mites have a preference for synthetic materials while avoiding natural fillers for the most part.
Depending on the severity of your symptoms and reactions to dust mites, you can also consider investing in an air purifier. Consider one for the home as well as a smaller one to place in areas where you spend the most time. Those with dust mite sensitivities may also have to reconsider adopting pets since the fur of many animals can attract dust and therefore dust mites.
Go back to the Home Pest Control home page or email us for more info about Dust Mites

